In daily printing operations, a common phenomenon has attracted widespread attention: when using the same ink, equipment, materials, and keeping printing parameters constant, the color of the same item printed in the morning, noon, and evening often shows slight differences. The causes and solutions to this phenomenon are worthy of in-depth discussion.
According to research conducted by our company, fluctuations in ambient temperature are the core factor contributing to this phenomenon. Our company points out that temperature changes directly affect the viscosity of the ink, and such changes in ink viscosity will further impact the ejection force of the nozzles, ultimately resulting in differences in printed colors.
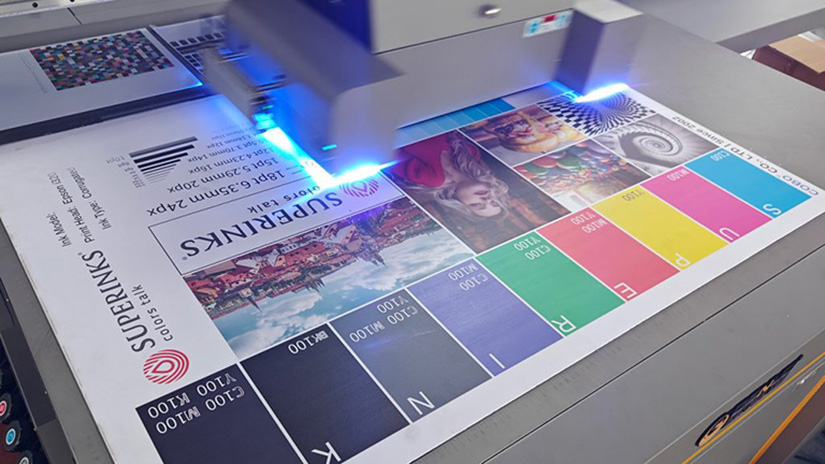

The viscosity of ink is highly sensitive to temperature. When the ambient temperature rises, the movement of ink molecules intensifies, internal friction decreases, leading to reduced viscosity and enhanced fluidity; conversely, when the temperature drops, molecular movement slows down, internal friction increases, resulting in higher viscosity and weakened fluidity.
Taking common water-based inkjet inks as an example, for every 5-10℃ temperature fluctuation, their viscosity may change by 10%-30%, which is sufficient to significantly affect printing results.
From the perspective of specific mechanisms, when high temperatures lead to low ink viscosity, the ink has strong fluidity and tends to spread when ejected from the nozzles. The speed of ink droplets increases, and their landing points are closer than expected, thereby increasing the ink volume per unit area and causing the color to appear darker;

when low temperatures result in high ink viscosity, the ink has poor fluidity, requiring the nozzles to exert greater ejection force. This, in turn, leads to slower ink droplet speed, farther landing points, and reduced ink volume per unit area, making the color look lighter.
In addition, temperature changes also affect the spreading and fusion of ink droplets on the material surface. In a high-temperature environment, ink droplets spread rapidly and may over-fuse with surrounding droplets, causing blurred edges and seemingly higher color saturation; in a low-temperature environment, ink droplets spread slowly with clearer edges, but due to insufficient fusion, the color may appear “dry” and the saturation will decrease accordingly.
This issue has caused many inconveniences in fields with high color accuracy requirements, such as advertising printing and packaging printing.
In response, a series of effective measures have been developed in the industry, and choosing an ink with strong adaptability to temperature changes is undoubtedly the key to solving the problem at its source.
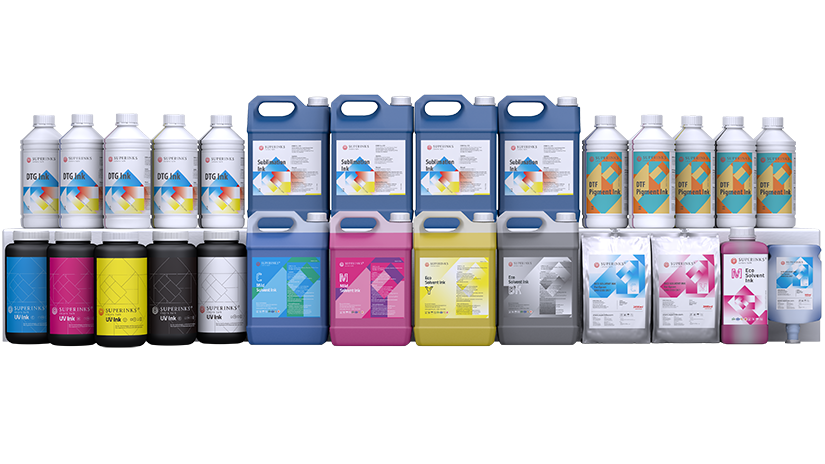

Here, we recommend our ink,
which excels in the adaptability of its viscosity to temperature changes. Compared with ordinary inks, our ink not only meets application needs under normal temperatures but also has distinct advantages in special temperature environments: in low-temperature environments, it can maintain low viscosity and better fluidity, avoiding problems such as poor ejection and lighter colors caused by high viscosity;
in high-temperature environments, its viscosity is relatively higher, making the ink less likely to break during ejection, reducing ink droplet spreading and darker colors, and effectively ensuring the stability of printed colors under different temperatures.
Besides selecting high-quality ink, other measures can be taken.
Firstly, control the printing environment temperature and keep it within the 15-25℃ range recommended for the ink, which can be achieved through air conditioning, heating, and constant-temperature equipment.
Secondly, perform constant-temperature treatment on the ink, such as equipping the ink container with a heating belt or a constant-temperature sleeve to ensure the ink temperature remains stable before entering the nozzles;
for large printing equipment, an ink circulation constant-temperature system can be installed for real-time adjustment. Some high-end printers are equipped with a “temperature-parameter linkage” function, which can dynamically adjust printing parameters according to temperature changes.
When the temperature rises, appropriately reduce the inkjet pressure or decrease the ink droplet volume to avoid excessive ink; when the temperature drops, appropriately increase the inkjet pressure or enlarge the ink droplet volume to compensate for insufficient ink.
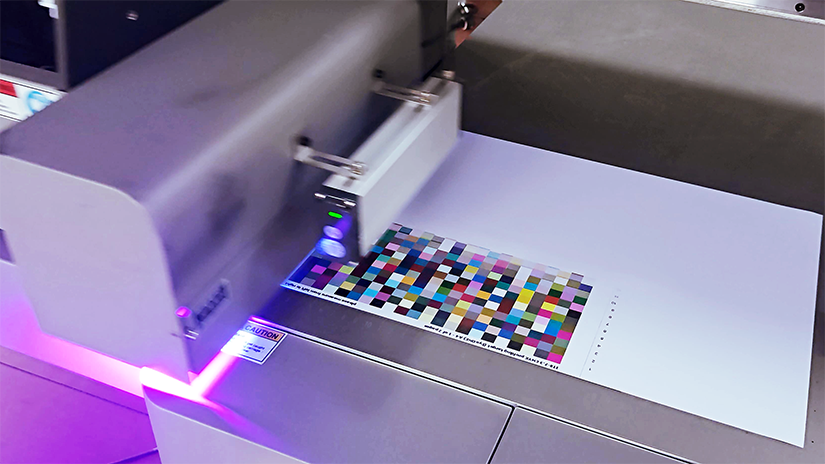
In addition, adjusting the ICC curve in the color management software using a printing calibration strip (such as a color card) to enable the system to automatically compensate for temperature-induced color differences can further improve the consistency of printing results. By mastering the above knowledge and using suitable ink, when encountering the situation where printed colors change over time, targeted measures can be taken to resolve it, thus ensuring the smooth progress of printing work.